UML Design
What is UML?
Section titled “What is UML?”-
UML stands for Unified Modeling Language.
-
It is used for Object-Oriented Analysis and Design (OOAD).
-
Helps to visualize, specify, construct, and document software systems.
-
UML consists of 13+ diagrams, categorized as:
-
Structural Diagrams (e.g., Class Diagram, Component Diagram)
-
Behavioral Diagrams (e.g., Use Case, Sequence Diagram)
-

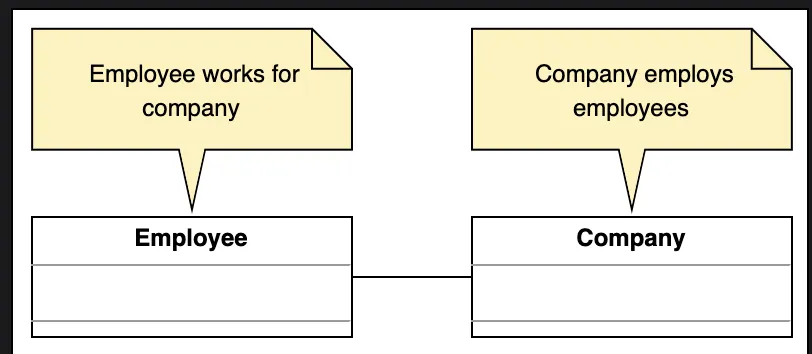
What is a Class Diagram?
Section titled “What is a Class Diagram?”Definition
Section titled “Definition”-
A Class Diagram represents the static structure of a system.
-
It models classes, their attributes, methods, and relationships between them.
Components
Section titled “Components”| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Class | Blueprint for objects |
| Attribute | Properties or data members |
| Method | Functions or operations of class |
| Relationships | Association, Aggregation, Composition, Inheritance |
Purpose
Section titled “Purpose”-
Helps in designing and understanding object-oriented systems.
-
Directly maps to OOP code (Java, C++, etc.).
Object Associations in UML
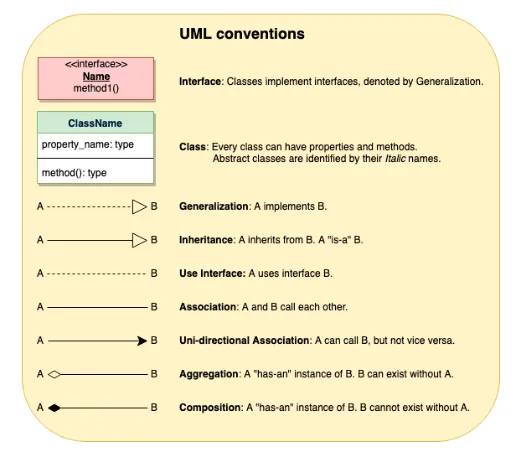
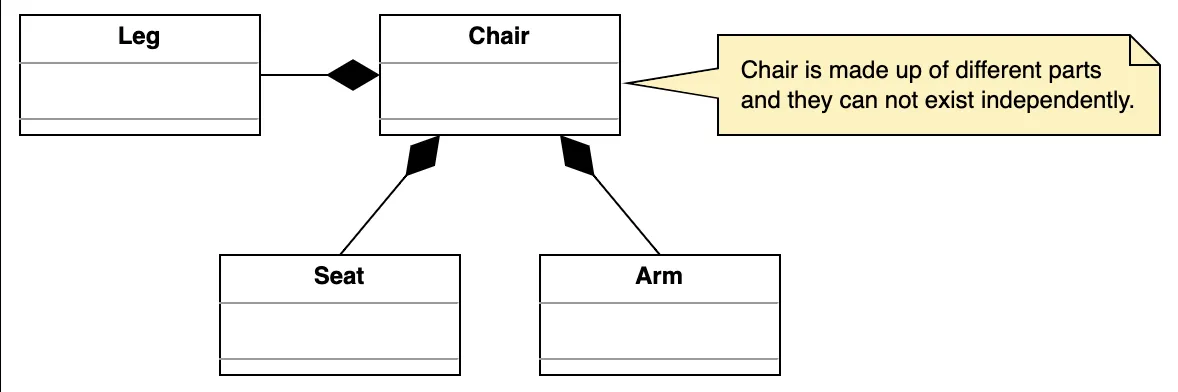
Section titled “Object Associations in UML”1. Composition (Strong Containment)
Section titled “1. Composition (Strong Containment)”“Has-a” relationship where lifetime is tightly bound.
-
One class owns another completely.
-
Child object cannot exist independently.
-
Represented using filled diamond.
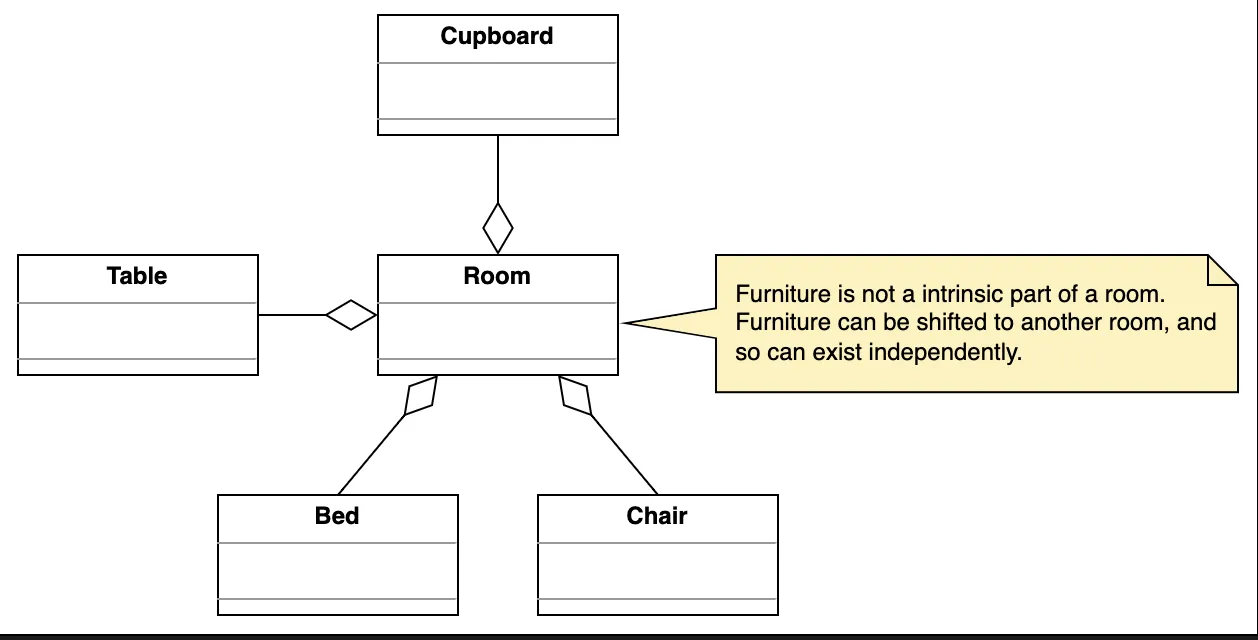
2. Aggregation (Weak Containment)
Section titled “2. Aggregation (Weak Containment)”“Has-a” relationship but with independent lifecycle.
-
One class contains another, but child can exist independently.
-
Represented using hollow diamond.
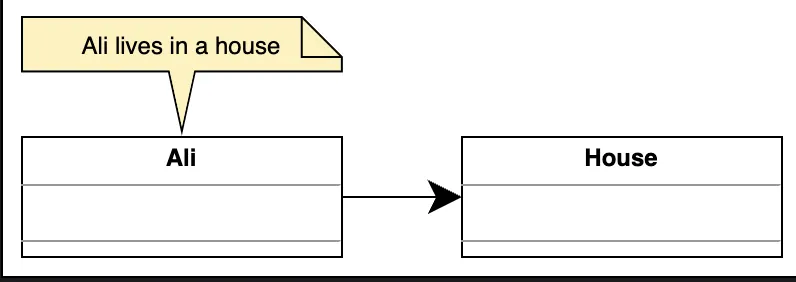
3. Association (Unidirectional)
Section titled “3. Association (Unidirectional)”One class knows about another.
-
Interaction flows in one direction only.
-
Represented using a simple arrow.
4. Association (Bidirectional)
Section titled “4. Association (Bidirectional)”Two classes are mutually aware.
-
Both classes can interact with each other.
-
Represented using a line without arrows.