⏳ Java Queue Interface - Complete Guide
“Queues are fundamental data structures that provide FIFO ordering, making them perfect for task scheduling, event processing, and producer-consumer patterns.”
🎯 What is the Queue Interface?
Section titled “🎯 What is the Queue Interface?”The Queue interface represents a collection designed for holding elements prior to processing. It extends the Collection interface and typically follows FIFO (First-In-First-Out) ordering, though some implementations like PriorityQueue use different ordering rules.
🔗 Key Characteristics
Section titled “🔗 Key Characteristics”| Feature | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| FIFO Ordering | First element in is first out | [a, b, c] → poll() returns a |
| Head Element | Single point of removal | poll(), peek() operate on head |
| Tail Addition | Elements added at the end | offer(x) adds to tail |
| Graceful Failure | Methods return null instead of throwing | poll() returns null if empty |
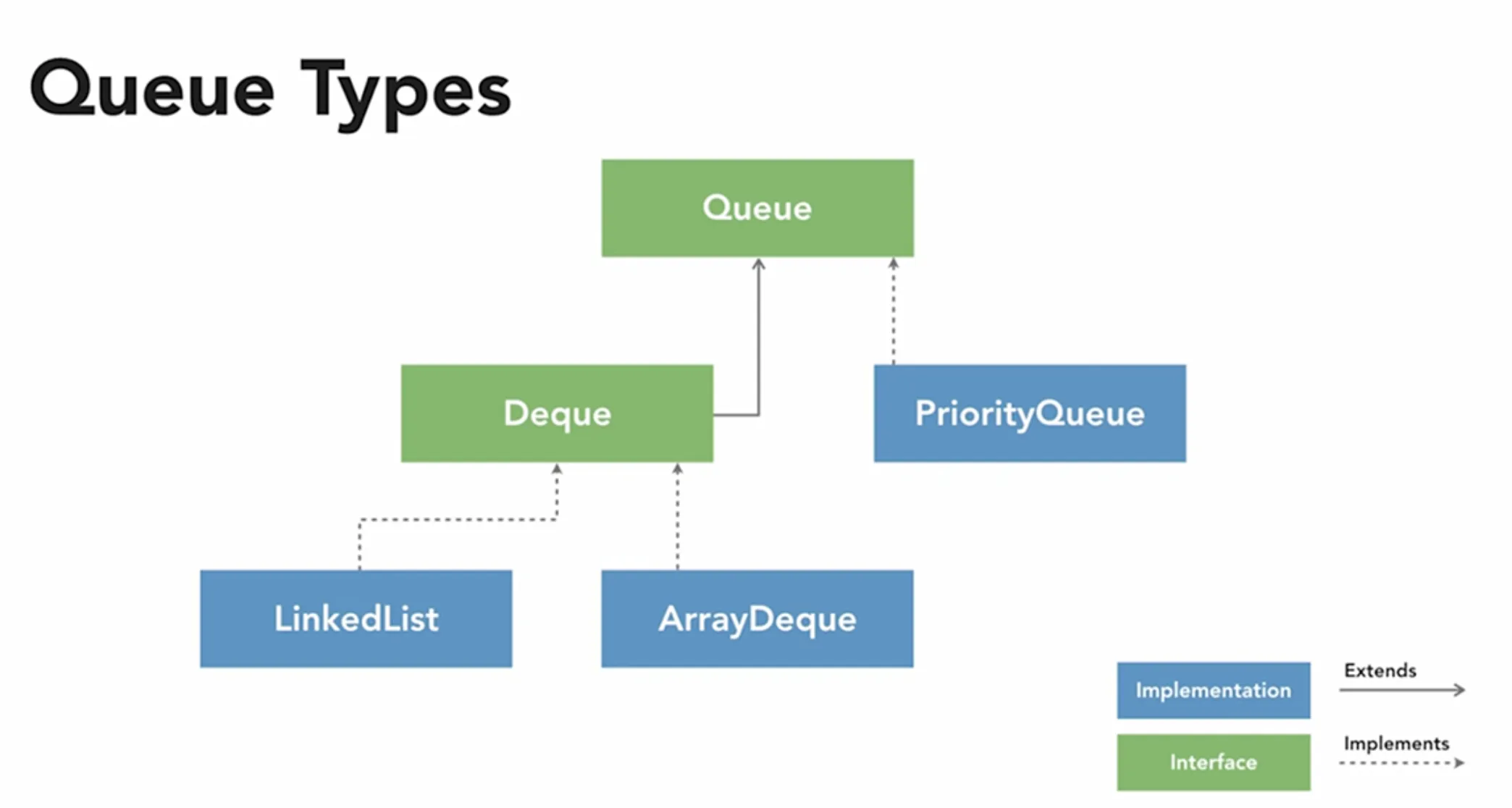
📊 Queue Hierarchy and Implementations
Section titled “📊 Queue Hierarchy and Implementations”🌳 Interface Hierarchy
Section titled “🌳 Interface Hierarchy”Collection<E>└── Queue<E> (interface) ├── PriorityQueue<E> - Heap-based priority queue ├── Deque<E> (interface) - Double-ended queue │ ├── ArrayDeque<E> - Resizable array deque │ ├── LinkedList<E> - Doubly-linked list deque │ └── LinkedBlockingDeque<E> - Blocking deque └── BlockingQueue<E> (interface) - Producer-consumer queues ├── ArrayBlockingQueue<E> - Bounded blocking queue ├── LinkedBlockingQueue<E> - Optionally bounded queue ├── PriorityBlockingQueue<E> - Unbounded priority blocking queue ├── DelayQueue<E> - Delayed elements queue ├── SynchronousQueue<E> - Zero-capacity handoff queue └── LinkedTransferQueue<E> - Transfer queue implementation📈 Performance Comparison Matrix
Section titled “📈 Performance Comparison Matrix”| Implementation | Offer | Poll | Peek | Size | Capacity | Thread Safe | Ordering |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ArrayDeque | O(1)* | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | Unlimited | ❌ | FIFO |
| LinkedList | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | Unlimited | ❌ | FIFO |
| PriorityQueue | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(1) | O(1) | Unlimited | ❌ | Priority |
| ArrayBlockingQueue | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | Bounded | ✅ | FIFO |
| LinkedBlockingQueue | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | Optionally bounded | ✅ | FIFO |
| PriorityBlockingQueue | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(1) | O(1) | Unlimited | ✅ | Priority |
* Amortized complexity - may be O(n) during resize
🔧 Queue Interface Methods
Section titled “🔧 Queue Interface Methods”
📋 Core Queue Methods
Section titled “📋 Core Queue Methods”public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> { // Insertion operations boolean add(E e); // Throws exception if fails (capacity restriction) boolean offer(E e); // Returns false if fails (preferred)
// Removal operations E remove(); // Throws NoSuchElementException if empty E poll(); // Returns null if empty (preferred)
// Examination operations E element(); // Throws NoSuchElementException if empty E peek(); // Returns null if empty (preferred)}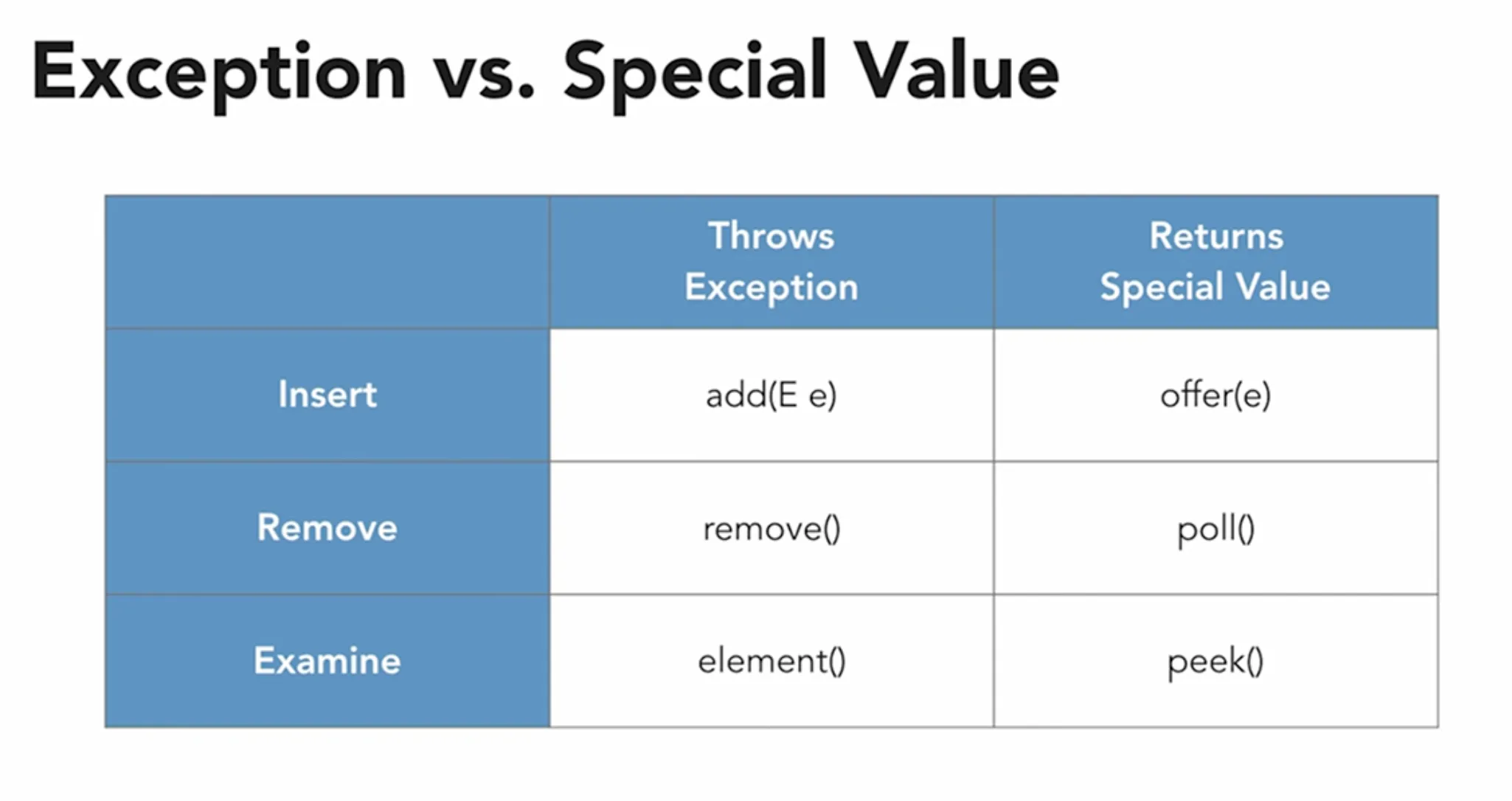
💻 Method Usage Examples
Section titled “💻 Method Usage Examples”public class QueueMethodExamples { public void demonstrateQueueMethods() { Queue<String> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// Adding elements (prefer offer over add) queue.offer("first"); // Safer - returns false if fails queue.offer("second"); queue.offer("third");
// Examining head element String head = queue.peek(); // "first" (doesn't remove) System.out.println("Head: " + head);
// Removing elements String removed = queue.poll(); // "first" (removes and returns) System.out.println("Removed: " + removed);
// Check if empty boolean isEmpty = queue.isEmpty(); int size = queue.size();
// Process all elements while (!queue.isEmpty()) { String element = queue.poll(); System.out.println("Processing: " + element); } }}🚀 ArrayDeque Implementation
Section titled “🚀 ArrayDeque Implementation”💡 What is ArrayDeque?
Section titled “💡 What is ArrayDeque?”ArrayDeque is a resizable array implementation of both Queue and Deque interfaces that provides:
- Fast operations at both ends (O(1) amortized)
- No capacity restrictions
- Efficient memory usage
- Better performance than Stack and LinkedList for most operations
🔧 ArrayDeque Construction
Section titled “🔧 ArrayDeque Construction”public class ArrayDequeConstructionExamples { public void demonstrateConstruction() { // Default constructor (initial capacity 16) ArrayDeque<String> deque1 = new ArrayDeque<>();
// With initial capacity ArrayDeque<String> deque2 = new ArrayDeque<>(100);
// From existing collection List<String> existing = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c"); ArrayDeque<String> deque3 = new ArrayDeque<>(existing);
// Using as Queue Queue<String> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// Using as Deque Deque<String> deque = new ArrayDeque<>(); }}📊 ArrayDeque Performance Characteristics
Section titled “📊 ArrayDeque Performance Characteristics”public class ArrayDequePerformanceExample { public void demonstratePerformance() { ArrayDeque<Integer> numbers = new ArrayDeque<>();
// Fast operations at both ends numbers.addFirst(1); // O(1) amortized numbers.addLast(100); // O(1) amortized numbers.removeFirst(); // O(1) numbers.removeLast(); // O(1)
// Queue operations numbers.offer(10); // O(1) amortized - adds to end numbers.offer(20); numbers.offer(30);
// Process queue while (!numbers.isEmpty()) { Integer number = numbers.poll(); // O(1) - removes from beginning System.out.println("Processing: " + number); }
// Stack operations numbers.push(1); // O(1) amortized - adds to beginning numbers.push(2); numbers.push(3);
while (!numbers.isEmpty()) { Integer number = numbers.pop(); // O(1) - removes from beginning System.out.println("Popped: " + number); } }}🔗 LinkedList as Queue
Section titled “🔗 LinkedList as Queue”💡 LinkedList Queue Capabilities
Section titled “💡 LinkedList Queue Capabilities”LinkedList implements both Queue and Deque interfaces, making it versatile for:
- Queue operations (FIFO)
- Deque operations (double-ended)
- List operations (indexed access)
- Dynamic sizing without capacity restrictions
🔧 LinkedList Queue Usage
Section titled “🔧 LinkedList Queue Usage”public class LinkedListQueueExamples { public void demonstrateLinkedListQueue() { // Using as Queue Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer("first"); queue.offer("second"); queue.offer("third");
// Process queue while (!queue.isEmpty()) { String element = queue.poll(); System.out.println("Processing: " + element); }
// Using as Deque Deque<String> deque = new LinkedList<>(); deque.addFirst("start"); deque.addLast("end"); deque.addFirst("newStart");
// Process from both ends while (!deque.isEmpty()) { String first = deque.removeFirst(); System.out.println("From start: " + first);
if (!deque.isEmpty()) { String last = deque.removeLast(); System.out.println("From end: " + last); } } }}🎯 PriorityQueue Implementation
Section titled “🎯 PriorityQueue Implementation”💡 What is PriorityQueue?
Section titled “💡 What is PriorityQueue?”PriorityQueue is a heap-based priority queue that provides:
- Priority-based ordering (not FIFO)
- Efficient insertion and removal of highest priority element
- Customizable ordering via Comparator
- Natural ordering for Comparable objects
🔧 PriorityQueue Construction
Section titled “🔧 PriorityQueue Construction”public class PriorityQueueConstructionExamples { public void demonstrateConstruction() { // Default constructor (natural ordering) PriorityQueue<Integer> numbers = new PriorityQueue<>();
// With initial capacity PriorityQueue<String> strings = new PriorityQueue<>(100);
// With custom comparator PriorityQueue<Integer> reverseOrder = new PriorityQueue<>( Comparator.reverseOrder() );
// From existing collection List<Integer> existing = Arrays.asList(5, 2, 8, 1, 9); PriorityQueue<Integer> fromList = new PriorityQueue<>(existing);
// Custom object with natural ordering PriorityQueue<Person> people = new PriorityQueue<>(); }}📊 PriorityQueue Performance Characteristics
Section titled “📊 PriorityQueue Performance Characteristics”public class PriorityQueuePerformanceExample { public void demonstratePerformance() { PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
// Insertion (O(log n)) queue.offer(5); queue.offer(2); queue.offer(8); queue.offer(1); queue.offer(9);
// Peek at highest priority (O(1)) Integer highest = queue.peek(); System.out.println("Highest priority: " + highest);
// Remove highest priority (O(log n)) while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Integer next = queue.poll(); System.out.println("Processing: " + next); }
// Custom priority queue PriorityQueue<String> customQueue = new PriorityQueue<>( (s1, s2) -> Integer.compare(s1.length(), s2.length()) );
customQueue.offer("short"); customQueue.offer("very long string"); customQueue.offer("medium");
// Process by string length (shortest first) while (!customQueue.isEmpty()) { String next = customQueue.poll(); System.out.println("Next by length: " + next); } }}📊 Decision Matrix
Section titled “📊 Decision Matrix”| Use Case | ArrayDeque | LinkedList | PriorityQueue | BlockingQueue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Queue | ✅ Best | ✅ Good | ❌ Wrong | ✅ Good |
| Performance | ✅ Best | ✅ Good | ⚠️ Good | ⚠️ Good |
| Memory Efficiency | ✅ Best | ❌ Poor | ✅ Good | ✅ Good |
| Priority Ordering | ❌ Wrong | ❌ Wrong | ✅ Best | ✅ Good |
| Thread Safety | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Best |
| List Operations | ❌ No | ✅ Best | ❌ No | ❌ No |