🌿 Java Set Interface - Complete Guide
“Sets provide efficient collections of unique elements, perfect for membership testing, duplicate removal, and mathematical set operations.”
🎯 What is the Set Interface?
Section titled “🎯 What is the Set Interface?”The Set interface represents a collection that contains no duplicate elements. It models the mathematical set abstraction and provides operations for union, intersection, and difference. Sets are primarily used for membership testing and eliminating duplicates.
🔗 Key Characteristics
Section titled “🔗 Key Characteristics”| Feature | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Unique Elements | No duplicates allowed | {a, b, c} not {a, b, a} |
| Mathematical Operations | Union, intersection, difference | {a,b} ∪ {b,c} = {a,b,c} |
| Membership Testing | Fast contains() operation | set.contains(x) |
| At Most One Null | Maximum one null element | {null, a, b} is valid |
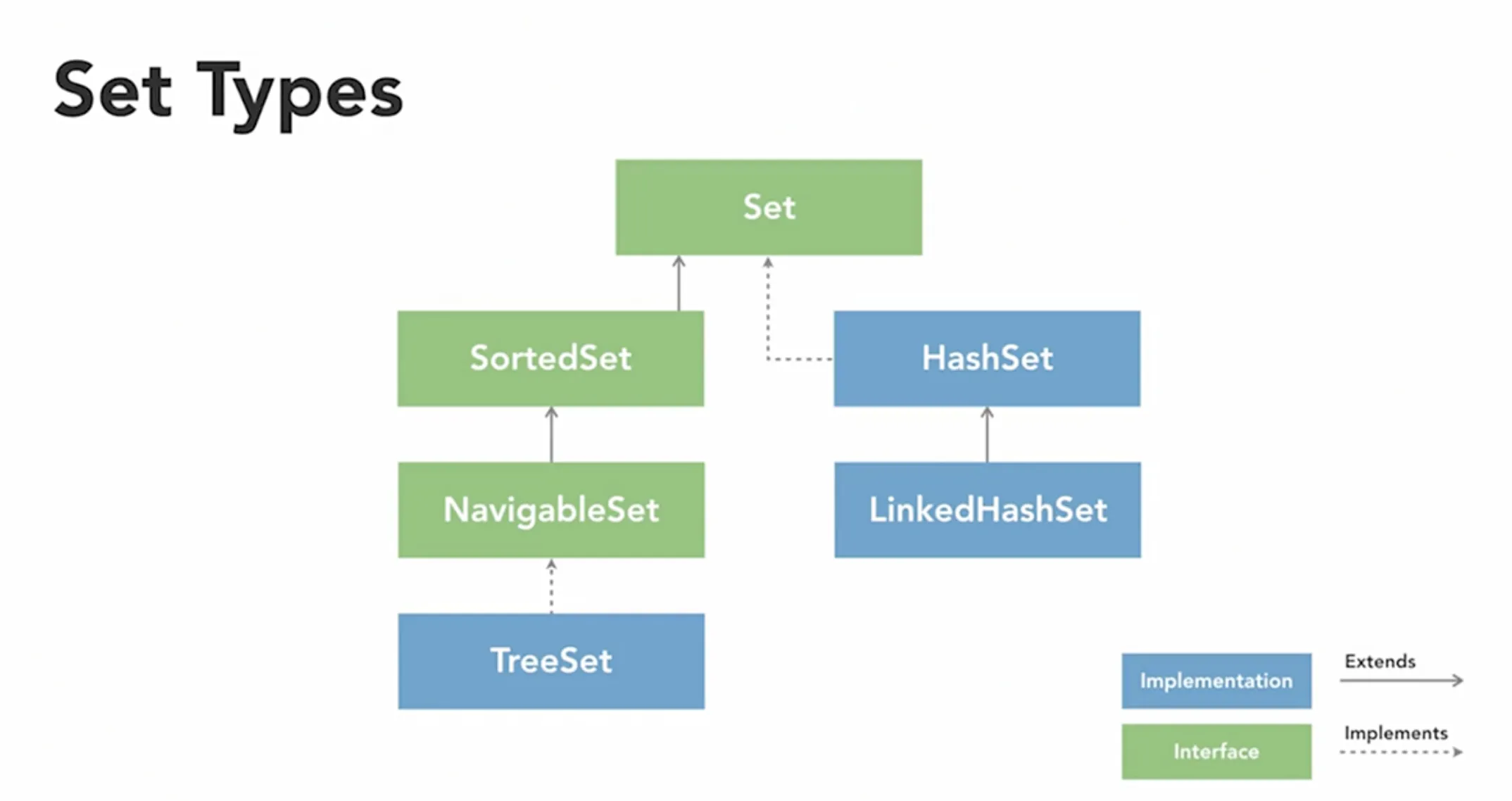
📊 Set Hierarchy and Implementations
Section titled “📊 Set Hierarchy and Implementations”🌳 Interface Hierarchy
Section titled “🌳 Interface Hierarchy”Collection<E>└── Set<E> (interface) ├── HashSet<E> - Hash table implementation, O(1) operations ├── LinkedHashSet<E> - Maintains insertion order ├── SortedSet<E> (interface) │ └── NavigableSet<E> (interface) │ └── TreeSet<E> - Red-black tree, sorted elements ├── EnumSet<E> - Specialized for enum types └── CopyOnWriteArraySet<E> - Thread-safe, read-optimized📈 Performance Comparison Matrix
Section titled “📈 Performance Comparison Matrix”| Implementation | Add | Remove | Contains | Iteration | Memory | Thread Safe | Ordering | Null Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HashSet | O(1)* | O(1)* | O(1)* | O(n) | Medium | ❌ | No | ✅ One null |
| LinkedHashSet | O(1)* | O(1)* | O(1)* | O(n) | High | ❌ | Insertion | ✅ One null |
| TreeSet | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(n) | Medium | ❌ | Sorted | ❌ No nulls |
| EnumSet | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | Very Low | ❌ | Declaration | ❌ No nulls |
| CopyOnWriteArraySet | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) | High | ✅ | Insertion | ✅ Nulls OK |
* Average case - worst case O(n) due to hash collisions
🔧 Set Interface Methods
Section titled “🔧 Set Interface Methods”📋 Core Set Methods
Section titled “📋 Core Set Methods”public interface Set<E> extends Collection<E> { // Basic operations (inherited from Collection) boolean add(E e); // Returns false if already present boolean remove(Object o); boolean contains(Object o); int size(); boolean isEmpty(); Iterator<E> iterator();
// Bulk operations boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c); boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c); // Union boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c); // Intersection boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c); // Difference void clear();
// Array conversion Object[] toArray(); <T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
// Java 8+ additions (inherited from Collection) default boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter); default Stream<E> stream(); default Stream<E> parallelStream();}💻 Mathematical Set Operations
Section titled “💻 Mathematical Set Operations”public class SetMathematicalOperations {
public void demonstrateSetOperations() { Set<String> set1 = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c", "d")); Set<String> set2 = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList("c", "d", "e", "f"));
// Union (A ∪ B) - all elements from both sets Set<String> union = new HashSet<>(set1); union.addAll(set2); System.out.println("Union: " + union); // [a, b, c, d, e, f]
// Intersection (A ∩ B) - common elements Set<String> intersection = new HashSet<>(set1); intersection.retainAll(set2); System.out.println("Intersection: " + intersection); // [c, d]
// Difference (A - B) - elements in A but not in B Set<String> difference = new HashSet<>(set1); difference.removeAll(set2); System.out.println("Difference: " + difference); // [a, b]
// Symmetric difference (A △ B) - elements in either A or B but not both Set<String> symmetricDiff = new HashSet<>(union); symmetricDiff.removeAll(intersection); System.out.println("Symmetric Difference: " + symmetricDiff); // [a, b, e, f]
// Subset check boolean isSubset = set1.containsAll(intersection); // true System.out.println("Intersection is subset of set1: " + isSubset); }}🚀 HashSet Implementation
Section titled “🚀 HashSet Implementation”💡 What is HashSet?
Section titled “💡 What is HashSet?”HashSet is a hash table-based implementation of the Set interface that provides:
- O(1) average case operations for add, remove, and contains
- No ordering guarantees
- Efficient memory usage
- Fast membership testing
🔧 HashSet Construction
Section titled “🔧 HashSet Construction”public class HashSetConstructionExamples { public void demonstrateConstruction() { // Default constructor (initial capacity 16, load factor 0.75) HashSet<String> set1 = new HashSet<>();
// With initial capacity HashSet<String> set2 = new HashSet<>(100);
// With initial capacity and load factor HashSet<String> set3 = new HashSet<>(100, 0.8f);
// From existing collection List<String> existing = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c"); HashSet<String> set4 = new HashSet<>(existing);
// Using factory methods (Java 9+) Set<String> immutableSet = Set.of("x", "y", "z"); HashSet<String> mutableSet = new HashSet<>(immutableSet); }}📊 HashSet Performance Characteristics
Section titled “📊 HashSet Performance Characteristics”public class HashSetPerformanceExample { public void demonstratePerformance() { HashSet<String> names = new HashSet<>();
// Fast insertion (O(1) average) names.add("Alice"); names.add("Bob"); names.add("Charlie"); names.add("David");
// Fast membership testing (O(1) average) boolean hasAlice = names.contains("Alice"); // true boolean hasEve = names.contains("Eve"); // false
// Fast removal (O(1) average) boolean removed = names.remove("Bob");
// Duplicate elements are ignored boolean added = names.add("Alice"); // false - already exists System.out.println("Size after duplicate add: " + names.size()); // Still 3
// Bulk operations Set<String> moreNames = Set.of("Eve", "Frank", "Grace"); names.addAll(moreNames);
// Iteration (order not guaranteed) for (String name : names) { System.out.println("Name: " + name); } }}🔗 LinkedHashSet Implementation
Section titled “🔗 LinkedHashSet Implementation”💡 What is LinkedHashSet?
Section titled “💡 What is LinkedHashSet?”LinkedHashSet extends HashSet to maintain a doubly-linked list that preserves:
- Insertion order of elements
- HashSet performance characteristics
- Predictable iteration order
- Higher memory overhead than HashSet
🔧 LinkedHashSet Usage
Section titled “🔧 LinkedHashSet Usage”public class LinkedHashSetExamples { public void demonstrateLinkedHashSet() { LinkedHashSet<String> orderedSet = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// Add elements in specific order orderedSet.add("first"); orderedSet.add("second"); orderedSet.add("third"); orderedSet.add("fourth");
// Iteration preserves insertion order System.out.println("Insertion order preserved:"); for (String item : orderedSet) { System.out.print(item + " "); // first second third fourth } System.out.println();
// Remove and re-add (maintains order) orderedSet.remove("second"); orderedSet.add("second");
System.out.println("After remove and re-add:"); for (String item : orderedSet) { System.out.print(item + " "); // first third fourth second } System.out.println();
// From existing collection List<String> list = Arrays.asList("zebra", "apple", "banana"); LinkedHashSet<String> fromList = new LinkedHashSet<>(list);
System.out.println("From list (preserves list order):"); for (String item : fromList) { System.out.print(item + " "); // zebra apple banana } System.out.println(); }}🌳 TreeSet Implementation
Section titled “🌳 TreeSet Implementation”💡 What is TreeSet?
Section titled “💡 What is TreeSet?”TreeSet is a red-black tree-based implementation that provides:
- Sorted elements in natural order or custom comparator
- O(log n) operations for add, remove, and contains
- Navigable operations (ceiling, floor, higher, lower)
- No null elements allowed
🔧 TreeSet Construction
Section titled “🔧 TreeSet Construction”public class TreeSetConstructionExamples { public void demonstrateConstruction() { // Default constructor (natural ordering) TreeSet<Integer> numbers = new TreeSet<>();
// With custom comparator TreeSet<String> reverseOrder = new TreeSet<>(Comparator.reverseOrder());
// With initial collection List<Integer> existing = Arrays.asList(5, 2, 8, 1, 9); TreeSet<Integer> fromList = new TreeSet<>(existing);
// Custom object with natural ordering TreeSet<Person> people = new TreeSet<>();
// Using NavigableSet methods NavigableSet<Integer> navigableSet = new TreeSet<>(); }}📊 TreeSet Performance Characteristics
Section titled “📊 TreeSet Performance Characteristics”public class TreeSetPerformanceExample { public void demonstratePerformance() { TreeSet<Integer> sortedSet = new TreeSet<>();
// Insertion (O(log n)) sortedSet.add(5); sortedSet.add(2); sortedSet.add(8); sortedSet.add(1); sortedSet.add(9);
// Elements are automatically sorted System.out.println("Sorted elements:"); for (Integer num : sortedSet) { System.out.print(num + " "); // 1 2 5 8 9 } System.out.println();
// Navigable operations Integer ceiling = sortedSet.ceiling(6); // 8 (smallest >= 6) Integer floor = sortedSet.floor(6); // 5 (largest <= 6) Integer higher = sortedSet.higher(5); // 8 (smallest > 5) Integer lower = sortedSet.lower(5); // 2 (largest < 5)
System.out.println("Ceiling(6): " + ceiling); System.out.println("Floor(6): " + floor); System.out.println("Higher(5): " + higher); System.out.println("Lower(5): " + lower);
// Subset operations NavigableSet<Integer> subset = sortedSet.subSet(2, true, 8, true); System.out.println("Subset [2,8]: " + subset); // [2, 5, 8]
// Head and tail sets SortedSet<Integer> headSet = sortedSet.headSet(5); SortedSet<Integer> tailSet = sortedSet.tailSet(5);
System.out.println("Head set < 5: " + headSet); // [1, 2] System.out.println("Tail set >= 5: " + tailSet); // [5, 8, 9] }}📊 Decision Matrix
Section titled “📊 Decision Matrix”| Use Case | HashSet | LinkedHashSet | TreeSet | EnumSet | CopyOnWriteArraySet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Purpose | ✅ Best | ✅ Good | ⚠️ Good | ❌ Wrong | ⚠️ Good |
| Performance | ✅ Best | ✅ Good | ⚠️ Good | ✅ Best | ❌ Poor |
| Memory Efficiency | ✅ Best | ❌ Poor | ✅ Good | ✅ Best | ❌ Poor |
| Ordering | ❌ No | ✅ Insertion | ✅ Sorted | ✅ Declaration | ✅ Insertion |
| Thread Safety | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Best |
| Range Queries | ❌ Poor | ❌ Poor | ✅ Best | ❌ Poor | ❌ Poor |