🧱 Java Stack Operations - Complete Guide
“Stacks provide efficient LIFO data structures perfect for function calls, expression evaluation, and backtracking algorithms.”
🎯 What is a Stack?
Section titled “🎯 What is a Stack?”A Stack is a linear data structure that follows the LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) principle. Elements are added and removed from the same end, called the “top” of the stack. Think of it like a stack of plates - you can only add or remove plates from the top.
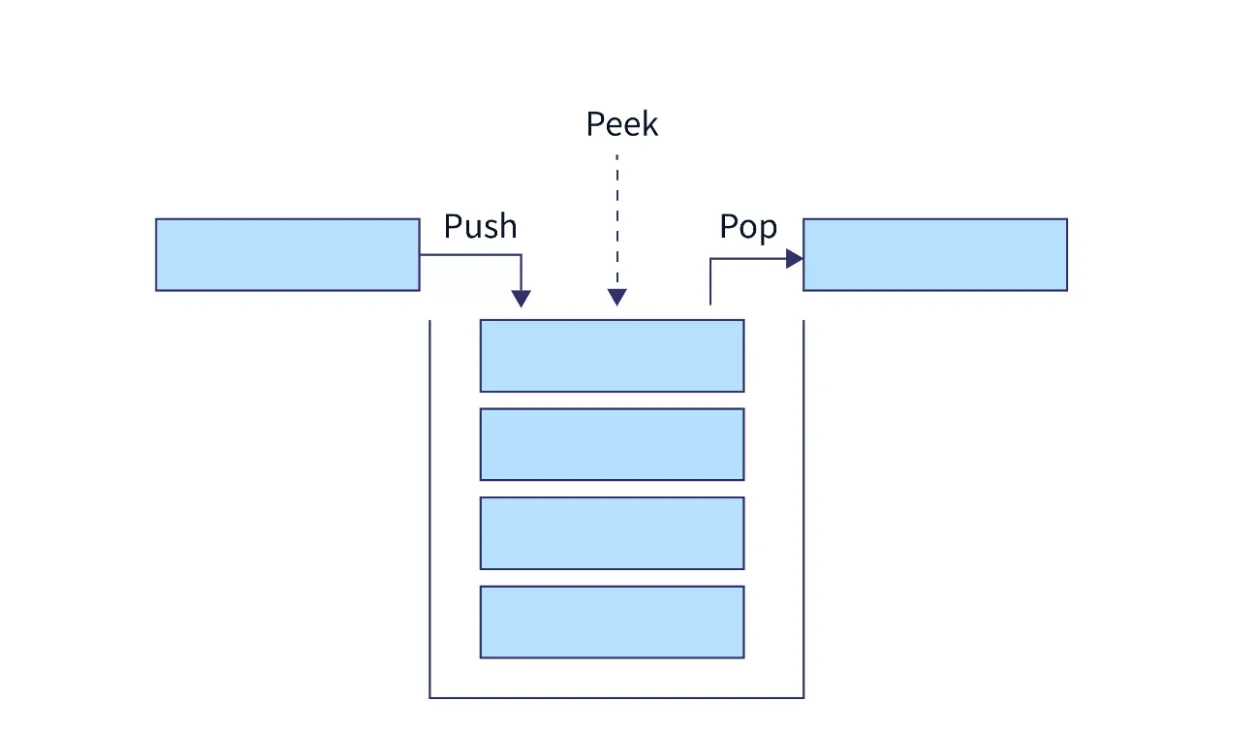
🔗 Key Characteristics
Section titled “🔗 Key Characteristics”| Feature | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| LIFO Ordering | Last element in is first out | push(a), push(b), pop() → b |
| Single Access Point | Operations only at the top | No middle element access |
| Principal Operations | push, pop, peek/top | Add, remove, examine top |
| Stack Overflow/Underflow | Capacity limits and empty checks | Handle bounds appropriately |
📊 Stack Implementation Options
Section titled “📊 Stack Implementation Options”🌳 Available Implementations
Section titled “🌳 Available Implementations”Stack Implementations in Java:├── Stack<E> (class) - Legacy synchronized stack│ └── Extends Vector<E> - Inherits all Vector methods├── Deque<E> implementations (modern approach)│ ├── ArrayDeque<E> - Recommended for stack operations│ ├── LinkedList<E> - Also implements Deque│ └── LinkedBlockingDeque<E> - Thread-safe deque└── Custom implementations - For specific requirements📈 Performance Comparison Matrix
Section titled “📈 Performance Comparison Matrix”| Implementation | Push | Pop | Peek | Access | Memory | Thread Safe | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stack | O(1)* | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | Medium | ✅ | ❌ Avoid (legacy) |
| ArrayDeque | O(1)* | O(1) | O(1) | N/A | Low | ❌ | ✅ Preferred |
| LinkedList | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | O(n) | High | ❌ | ⚠️ Acceptable |
| LinkedBlockingDeque | O(1) | O(1) | O(1) | N/A | High | ✅ | ✅ For concurrency |
* Amortized complexity - may be O(n) during resize
🔧 Stack Operations
Section titled “🔧 Stack Operations”📋 Essential Stack Methods
Section titled “📋 Essential Stack Methods”// Stack Interface Contract (conceptual)public interface StackOperations<E> { void push(E element); // Add element to top E pop(); // Remove and return top element E peek(); // Return top element without removing boolean isEmpty(); // Check if stack is empty int size(); // Return number of elements}💻 Basic Stack Operations
Section titled “💻 Basic Stack Operations”public class StackOperationsExamples {
public void demonstrateStackOperations() { // Using ArrayDeque as stack (recommended) Deque<String> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
// Push operations - add to top stack.push("bottom"); // Stack: [bottom] stack.push("middle"); // Stack: [middle, bottom] stack.push("top"); // Stack: [top, middle, bottom]
System.out.println("Stack: " + stack);
// Peek operation - examine top without removing String topElement = stack.peek(); // "top" System.out.println("Top element: " + topElement); System.out.println("Size after peek: " + stack.size()); // Still 3
// Pop operations - remove from top String popped1 = stack.pop(); // "top", Stack: [middle, bottom] String popped2 = stack.pop(); // "middle", Stack: [bottom] String popped3 = stack.pop(); // "bottom", Stack: []
System.out.println("Popped: " + popped1 + ", " + popped2 + ", " + popped3); System.out.println("Is empty: " + stack.isEmpty()); // true
// Safe operations if (!stack.isEmpty()) { String safe = stack.pop(); }
String safepeek = stack.peek(); // Returns null if empty (ArrayDeque) if (safepeek != null) { System.out.println("Safe peek: " + safepeek); } }}🚀 ArrayDeque as Stack (Recommended)
Section titled “🚀 ArrayDeque as Stack (Recommended)”💡 Why ArrayDeque?
Section titled “💡 Why ArrayDeque?”ArrayDeque is the modern, preferred implementation for stack operations because it:
- Implements Deque interface with stack methods
- Better performance than legacy Stack class
- No synchronization overhead
- Memory efficient with resizable array
- Part of modern collections framework
🔧 ArrayDeque Stack Usage
Section titled “🔧 ArrayDeque Stack Usage”public class ArrayDequeStackExamples { public void demonstrateArrayDequeStack() { // Create stack using ArrayDeque Deque<String> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
// Stack operations stack.push("first"); stack.push("second"); stack.push("third");
System.out.println("Stack contents: " + stack); System.out.println("Stack size: " + stack.size()); System.out.println("Is empty: " + stack.isEmpty());
// Examine top element String top = stack.peek(); System.out.println("Top element: " + top);
// Process stack (LIFO order) System.out.println("Processing stack (LIFO order):"); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { String element = stack.pop(); System.out.println("Popped: " + element); }
// Stack is now empty System.out.println("Stack is empty: " + stack.isEmpty()); System.out.println("Stack size: " + stack.size()); }}📊 ArrayDeque Performance Characteristics
Section titled “📊 ArrayDeque Performance Characteristics”public class ArrayDequePerformanceExample { public void demonstratePerformance() { Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
// Fast push operations (O(1) amortized) long start = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { stack.push(i); } long pushTime = System.nanoTime() - start;
// Fast pop operations (O(1)) start = System.nanoTime(); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { stack.pop(); } long popTime = System.nanoTime() - start;
System.out.printf("Push time: %d ns%n", pushTime); System.out.printf("Pop time: %d ns%n", popTime);
// Memory efficiency System.out.println("Final size: " + stack.size()); // 0 }}🔗 LinkedList as Stack
Section titled “🔗 LinkedList as Stack”💡 LinkedList Stack Capabilities
Section titled “💡 LinkedList Stack Capabilities”LinkedList implements Deque and can be used as a stack, providing:
- Stack operations (push, pop, peek)
- Dynamic sizing without capacity restrictions
- Higher memory overhead than ArrayDeque
- Flexible structure for frequent modifications
🔧 LinkedList Stack Usage
Section titled “🔧 LinkedList Stack Usage”public class LinkedListStackExamples { public void demonstrateLinkedListStack() { // Using LinkedList as stack Deque<String> stack = new LinkedList<>();
// Stack operations stack.push("bottom"); stack.push("middle"); stack.push("top");
System.out.println("LinkedList stack: " + stack);
// Process in LIFO order while (!stack.isEmpty()) { String element = stack.pop(); System.out.println("Popped: " + element); }
// LinkedList also supports other operations LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<>(); linkedList.push("first"); linkedList.push("second");
// Can access elements by index (but not recommended for stack usage) String first = linkedList.get(0); String last = linkedList.get(linkedList.size() - 1);
System.out.println("First: " + first + ", Last: " + last); }}🧱 Legacy Stack Class
Section titled “🧱 Legacy Stack Class”💡 What is the Stack Class?
Section titled “💡 What is the Stack Class?”The Stack class is a legacy implementation that extends Vector and provides:
- Synchronized operations (thread-safe but slower)
- Legacy methods from Vector
- Deprecated design (not recommended for new code)
- Better alternatives available in modern Java
🔧 Legacy Stack Usage
Section titled “🔧 Legacy Stack Usage”public class LegacyStackExamples { public void demonstrateLegacyStack() { // Legacy Stack class (not recommended) Stack<String> legacyStack = new Stack<>();
// Basic stack operations legacyStack.push("first"); legacyStack.push("second"); legacyStack.push("third");
// Examine top element String top = legacyStack.peek(); System.out.println("Top element: " + top);
// Pop elements while (!legacyStack.isEmpty()) { String element = legacyStack.pop(); System.out.println("Popped: " + element); }
// Legacy methods (inherited from Vector) legacyStack.add("legacy"); // add() method legacyStack.insertElementAt("inserted", 0); // insertElementAt() legacyStack.removeElementAt(0); // removeElementAt()
// Search method (returns 1-based position from top) legacyStack.push("searchable"); int position = legacyStack.search("searchable"); // 1 (top) System.out.println("Position from top: " + position); }}⚠️ Why Avoid Legacy Stack
Section titled “⚠️ Why Avoid Legacy Stack”public class LegacyStackProblems { public void demonstrateProblems() { // 1. Synchronization overhead (even in single-threaded code) Stack<String> slowStack = new Stack<>();
long start = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { slowStack.push("item" + i); } long stackTime = System.nanoTime() - start;
// Compare with ArrayDeque Deque<String> fastStack = new ArrayDeque<>(); start = System.nanoTime(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { fastStack.push("item" + i); } long dequeTime = System.nanoTime() - start;
System.out.printf("Stack: %d ns, ArrayDeque: %d ns%n", stackTime, dequeTime);
// 2. Inherits Vector methods that don't make sense for stacks Stack<String> confusingStack = new Stack<>(); confusingStack.push("first"); confusingStack.push("second");
// These methods break stack semantics confusingStack.add(0, "inserted"); // Insert at bottom confusingStack.remove(1); // Remove from middle
System.out.println("Confusing stack: " + confusingStack);
// 3. Better alternatives available // Use ArrayDeque for single-threaded stacks // Use LinkedBlockingDeque for thread-safe stacks }}📊 Decision Matrix
Section titled “📊 Decision Matrix”| Use Case | ArrayDeque | LinkedList | LinkedBlockingDeque | Legacy Stack |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-threaded | ✅ Best | ✅ Good | ⚠️ Overkill | ❌ Avoid |
| Performance | ✅ Best | ✅ Good | ⚠️ Good | ❌ Poor |
| Memory Efficiency | ✅ Best | ❌ Poor | ❌ Poor | ⚠️ Good |
| Thread Safety | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Best | ✅ Yes |
| Modern Design | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |