Java Asynchronous Programming
🚀 Introduction
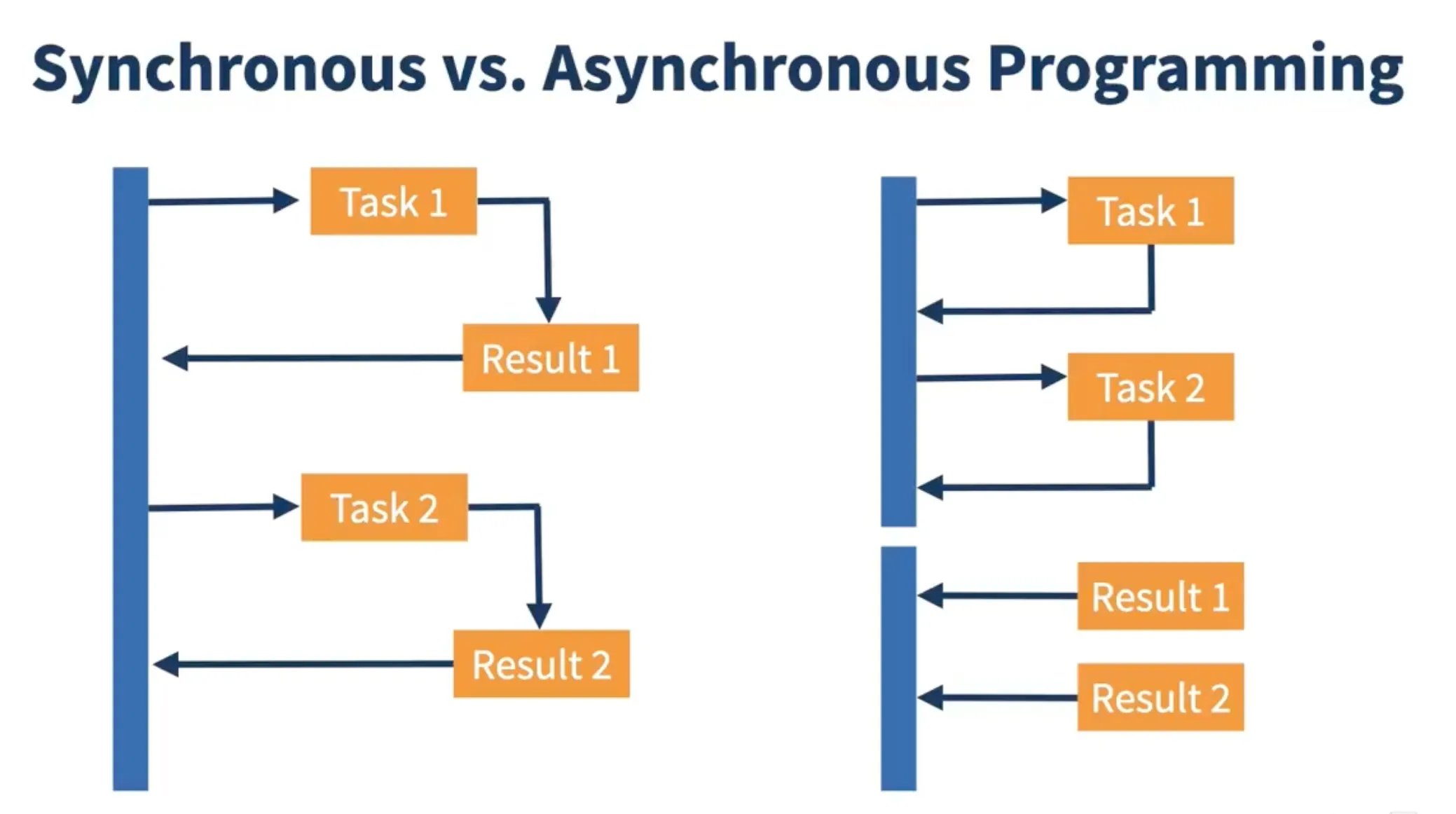
Section titled “🚀 Introduction”🔄 What is Asynchronous Programming?
Section titled “🔄 What is Asynchronous Programming?”Asynchronous programming allows tasks to run in the background without stopping the main thread. This enables:
- 🧵 Non-blocking execution
- ⚡ Better resource use
- 💻 Smooth user interfaces
- 📈 High scalability for concurrent tasks
- Goal → better responsiveness and parallelism
🔁 Synchronous vs Asynchronous
Section titled “🔁 Synchronous vs Asynchronous”| Feature | Synchronous | Asynchronous |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Blocking, sequential | Non-blocking, concurrent |
| Thread Usage | Single | Multiple |
| UI Responsiveness | May block | Remains responsive |
| Complexity | Simple | Requires more control |
| Error Handling | try-catch | callbacks, handlers |
✅ When to Use Async Code
Section titled “✅ When to Use Async Code”- I/O operations (network, file, DB)
- CPU-heavy tasks (math, ML)
- UI apps (to avoid freezing)
- Backend services (handle many requests)
👉 Example (Real-life analogy):
-
Synchronous: Order coffee → wait until it’s made → then do other work.
-
Asynchronous: Order coffee → work on laptop → barista notifies you when coffee is ready.
☎️ Callable Interface (Why not Runnable?)
Section titled “☎️ Callable Interface (Why not Runnable?)”⚖ Callable vs Runnable
Section titled “⚖ Callable vs Runnable”| Feature | Callable | Runnable |
|---|---|---|
| Returns value | ✅ Yes (V) | ❌ No |
| Throws Exception | ✅ Yes (checked exceptions allowed) | ❌ No (only unchecked) |
| Generics | ✅ Supports generics | ❌ No |
| Introduced in | Java 5 | Java 1.0 |
🔍 Overview
Section titled “🔍 Overview”-
Callable<V>is likeRunnablebut:-
Can return a result (
V) -
Can throw checked exceptions
-
-
Designed for asynchronous tasks that produce a result.
✨ Key Features
Section titled “✨ Key Features”-
✔ Returns result (
V) -
❗ Can throw checked exceptions
-
🧠 Uses generics for type safety
Future & Callable
Section titled “Future & Callable”-
Runnablecannot return results. -
Callablecan return a value + throw exceptions. -
Futureholds the result of asynchronous computation.
☎️ Callable Interface (Why not Runnable)
Section titled “☎️ Callable Interface (Why not Runnable)”import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CallableExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Callable<String> task = () -> "Hello from Callable!";
FutureTask<String> future = new FutureTask<>(task); new Thread(future).start();
String result = future.get(); // Waits for result System.out.println(result); }}🔮 Future Interface
Section titled “🔮 Future Interface”Future represents the result of an async task, which will be available later.
🛠 Key Methods
Section titled “🛠 Key Methods”get()– wait for resultcancel()– try to stopisDone()– check completionisCancelled()– check cancel
🚦 Example
Section titled “🚦 Example”Future<Integer> f = executor.submit(() -> 42);Integer result = f.get(); // Waits here⏳ Timeout Example
Section titled “⏳ Timeout Example”future.get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // Throws TimeoutException if late⚠️ Limitations of Future
Section titled “⚠️ Limitations of Future”-
❌
get()is blocking → doesn’t feel truly async -
❌ No built-in chaining (cannot say do this after completion)
-
❌ No easy error handling (exceptions wrapped in
ExecutionException) -
❌ Cannot combine multiple futures (e.g., wait for both Task A & B)
👉 That’s why CompletableFuture (Java 8+) was introduced to overcome these issues.
✅ CompletableFuture
Section titled “✅ CompletableFuture”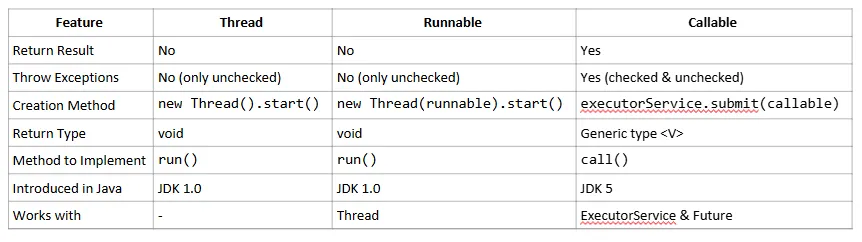
📚 Overview
Section titled “📚 Overview”CompletableFuture improves on Future by adding:
- ✅ Non-blocking chaining
- 🔗 Composability
- 💥 Error handling
- 🧪 Manual completion
🔑 Key Features
Section titled “🔑 Key Features”| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
thenApply | Transforms result |
thenAccept | Consumes result (no return) |
exceptionally | Handle errors |
thenCombine | Combine multiple futures |
allOf, anyOf | Wait for all/any futures |
🧪 Basic Example
Section titled “🧪 Basic Example”CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hi") .thenApply(data -> data.toUpperCase()) .thenAccept(System.out::println);🔁 Chaining & Error Handling
Section titled “🔁 Chaining & Error Handling”Use thenCompose() to chain dependent tasks, and exceptionally() to handle errors.
🔗 Combining Multiple Futures
Section titled “🔗 Combining Multiple Futures”thenCombine(f2, (a, b) -> a + b);CompletableFuture.allOf(f1, f2).join();🧵 Manual Completion
Section titled “🧵 Manual Completion”CompletableFuture<String> future = new CompletableFuture<>();future.complete("Done"); // Manually set result